How To Repair A Cut Verizon Internet And Tv Wire Thst Was Buried
What is Coaxial Cable?
Patented in 1880, coaxial cable has been a standard means of delivering high frequency electrical signals over distances with low point loss. It has many applications, including telephone trunk lines, cable tv set signals, and cell phone boosters. Cables come up in many sizes and lengths, each designed for a specific awarding.
Coaxial cable has an inner and outer core that share a geometric axis. This prevents electromagnetic interference and enables more reliable information transmission over longer distances.
See complete cell signal booster kits for your situation:

Abode
Vehicle

Business concern

Commercial
How is Coaxial Cable Constructed?
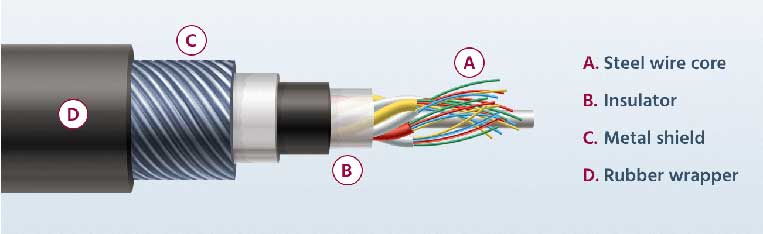
Coaxial cable is synthetic from a unmarried copper or copper-coated steel wire every bit the heart core which carries the high frequency signal. This wire is surrounded past a dielectric insulator, often made of plastic, which keeps a abiding distance between the center conductor and the next layer. This insulator is wrapped with a metal shield fabricated of woven copper, aluminum or other metallic. This cancels outside electromagnetic interference. The last layer is a rubber wrapper that insulates the whole configuration.
Coaxial cable tin can exist used in both indoor and outdoor applications with a few differences. Coax used outdoors requires additional insulation to protect the wires from sun and wet. Cables rated for outdoor utilize may run along the outside of your home to a satellite dish or to the cablevision box on the corner. Whether out in the sunday or buried in the earth, the cable needs to be protected enough to provide seamless transmissions.
How Does Coaxial Cable Work?
A coaxial cable carries a betoken which goes across the center copper wire too as the metal shield. Both of these metallic conductors generate a magnetic field. The insulators go along the signals from coming in contact with or cancelling out each other. The insulators also protect the point from outside magnetic fields. As a issue, the betoken is carried over long distances with little interference or signal loss.
What are the Uses and Applications of Coaxial Cables

Coaxial Cable is used by cablevision operators, telephone companies and net providers. If you take cable television, you have a coaxial cablevision installed in your home. Coaxial cables are also used for connecting VCRs to a goggle box or connecting your idiot box set or digital convertor box to a personal antenna.
Signal Boosters
Wilson Amplifiers is the leading provider of cell phone boosters. A coaxial cable is used to connect to a prison cell phone booster as well. An antenna is installed on the outside of your house, an amplifier boosts cell phone betoken on the inside of your business firm, a second antenna is installed on the inside of your business firm. The coaxial cable ties the three devices together. Using this technology, you can boost a weak cellular 3G & 4G signal. Information technology cannot create signal where there was none, nor can it boost a landline wi-fi signal.
Basic RF
RF is Radio Frequency. RF waves are generated when an alternating current goes through a conductive cloth. Coaxial cable carries radio frequency signals.
Cable net (copper-based)
Cablevision internet works off a coaxial cable. The copper-based cable is piped into your firm from the cable service provider. You then plug the connector into a router or cablevision modem, which then is plugged into your television or computer for cyberspace and cable viewing access.
Ham radio
Ham radio is a means for people to communicate over the air waves. Coaxial cable continued to the antenna provide a stronger indicate. Ham radios can be set up in the middle of nowhere and exercise not require the net or cell phone technology.
How Many Types of Coaxial Cables are At that place?
In that location are many unlike types of coaxial cablevision. Your application will determine which cable has the best characteristics. Consult with your user's transmission and specs of each type to make the best decision. There are hundreds of cables to choose from to fit every need yous have, merely here are a few mutual types.
If yous are very computing specific rates of loss or ohms, please see technical specs for each type.
Coaxial cable size chart
RG-six/U
Impedance: 75 Ohm
Core size: one.024 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: 5.650
LMR®400
Impedance: fifty Ohm
Cadre size: 2.74 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: 3.five
RG-8
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Core size: 1.024 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: five.650
LMR®600
Impedance: l Ohm
Core size: 4.47 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: 2.3
RG-eleven
Impedance: 75 Ohm
Cadre size: i.024 mm
Dielectric Blazon: PF
Max Attenuation: v.650
LMR®900
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Cadre size: vi.65 mm
Dielectric Blazon: PF
Max Attenuation: 2.5
LMR®200
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Core size: 1.12 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: nine.0
LMR®1200
Impedance: l Ohm
Core size: eight.86 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: ane.3
LMR®240
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Core size: one.42 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: half-dozen.9
LMR®1700
Impedance: 50 Ohm
Core size: 13.39 mm
Dielectric Type: PF
Max Attenuation: 0.eight
PE = solid polyethylene PF = polyethylene foam Max Attenuation (750 MHz (dB/100 ft)
RG-6/U
RG-6/U is a very common type of coaxial cable. Information technology has an impedance of 75 Ohm and is used in a wide diverseness of residential and commercial applications including cablevision television.
RG-8
RG-8 is similar to RG-6, but unable to behave pure video signals. It has an impedance of 50 Ohm and is used in sound control rooms, radio stations or as connections for external radio antennas.
RG-xi
RG-11 is a higher gauge cable used for CATV, HDTV, TV antennas and video distribution. It has an impedance of 75 Ohm and provides 3 GHz frequency.
LMR® is the newer generation of RF coaxial cables. They provide greater flexibility, ease of installation and lower cost. They are used as transmission lines for antennas on missiles, airplanes, ships, satellites and communications.
LMR®200
LMR®200 is an outdoor rated flexible low loss communications coax. Information technology has an impedance of 50 Ohm, and is great for short antenna feeder runs. This too has a feature of low PIM.
LMR®240
LMR®240 is also an outdoor rated flexible depression loss communications coax with an impedance of 50 Ohm. It is designed for short feeder runs for a variety of applications including GPS, WLAN, and Mobile Antennas.
LMR®400
LMR®400 is a flexible communications coax with an impedance of 50 Ohm. It is used for jumper assemblies in wireless communications Systems and short antenna feeder runs. If you demand a cablevision that requires periodic or repeated flexing, choose this ane. LMR®400 was designed to replace the RG-viii cables.
LMR®600
LMR®600 "Half Inch" is designed for outdoor employ likewise. It is more flexible that air-dielectric and hardline cables in terms of bending and treatment. Information technology too has an impedance of fifty Ohm.
LMR®900/ 1200/1700
LMR®900/1200/1700 are larger cables designed for medium antenna feeder runs with whatsoever application requiring an easily routed, flexible low loss cable.
Other Features of Coaxial Cables

Coaxial Cable Length
Coaxial cable comes in varying lengths. The shorter and thicker the cablevision is rated will decide the strength of the signal transmitted. It is important to cull the right cable length and thickness. In radio systems, cablevision length is comparable to the wavelength of the signals transmitted. Yous can report the math involved in deciding the all-time cable length to utilise. Characteristics of the cable, such and exterior diameter of the inner usher, inside diameter of the shield, dielectric contact of the insulator and magnetic permeability of the insulator all affect the quality of the wavelength going through your cable.
Coaxial cables and dBm
dBm stands for the ability ratio in decibels (dB) of the power measured to i milliwatt. Used in radio, microwave and fiber optic applications, this is the betoken forcefulness. The blazon of coaxial cable used volition determine your signal strength and how many dBm your cable can handle.
Coaxial cables and ohms and impedance
Impedance is the amount of resistance the waves proceeding through the coaxial cable encounters. The lower the impedance, the more hands the waves menstruation through the cablevision. Each type cable has an impedance rating. Factors affecting this is the size of the cable and what materials the cable is synthetic from. Standard coax impedances are fifty-75 ohms. This has been tested equally a neat rest between power handling a low loss.
Coaxial Cables and PIM
PIM stands for Passive Intermodulation. When you connect two metals, the result is nonlinear elements and a distortion in the signal may occur. As the point amplitude goes up, the furnishings volition be more significant. This happens oft when connecting antennas, cables and connectors. PIM issues occur most oft in LTE, HSPA and CDMA cellular networks.
What is a Coaxial Cable Connector?

Connectors are on each terminate of the cable. They are designed to maintain the integrity of the cable as it passed the point through to your device. They are ordinarily plated with high-connectivity metals such tarnish-resistant gold or silver. The type of connector you demand depends on what you are connecting to and how far from the source of power to the device.
A few general types of connectors include:
SMA
SMA stands for Subminiature Version A. This is a minimal connector interface for coaxial cable with a screw-blazon coupling mechanism. Information technology has an impedance of 50 Ohm and are designed for utilise from DC (0 Hz) to 18 GHz. Applications include microwave systems, handheld radios and mobile phone antennas.
F-Type Connector
F-Blazon Connector - this is a mid-size connector designed for common utilize. It is the most widely used connector for residential wiring and is used with cable television, satellite television and cablevision modems. It is commonly used with RG-half-dozen/U Cablevision.
N-Type Connector
N-Type Connector – this is a larger connector design to be used with thick, commercial cablevision.
Connectors are either male or female. Male connectors take threads on the inside of the shell and female connectors have threads on the outside of the crush. Check the plug on your device if information technology is female, you need a male plug and vice versa.
Putting It Together

RG6 Cables with F-Type Connectors
The RG6 cable is a 75 ohm cable with F-Blazon connectors. This is the same cable used with many Cable/Satellite Television receiver devices and comes pre-wired in many homes, making information technology unproblematic to wire and install.
The F-Type connector is a mid-size connector designed for common employ. It is the nigh widely used coaxial connector for residential wiring.
Mainly used for the boilerplate dwelling installation that covers 2,500 to five,000 sq ft. Cable length from twenty to fifty feet. Comes only in white.
These come kitted with the pop weBoost Home MultiRoom and the upkeep weBoost Home 4G.

RG11 Cables with F-Type Connectors
The RG11 cable is another 75 ohm cable with F-Type connectors. What separates information technology from the R6 is its range: whereas the R6 tops out at 50 feet, the RG11 ranges from fifty to 100 anxiety and features lower loss.
These do not come up pre-kitted with any of our point boosters, but are highly recommended if you lot believe it is probable you will be running over 50 feet of cablevision to ability your booster.

Wilson400 Cables with N-Type Connectors
The Wilson400 cable is an LMR®400 spec cable.
These are l-ohm, pro-grade coaxial cables designed for large installations from 7,500 to 50,000 foursquare feet. Cable length ranges from l to 1000 anxiety, spooled. Your installer will typically apportion the cable into shorter lengths to cover the range of the installation while maintaining quality signal strength.
This Wilson400 is fitted with an Northward-Type connector, a big connector designed to be used with thick, commercial cable.
The most popular units that include these cables are the weBoost Connect 4G-X and the WilsonPro line of commercial signal boosters. However, they are compatible with any equipment that uses 50 Ohm cables fitted with N-Connectors.

LMR®600 and LDF4/Al4 RPV-50 "Half Inch" with Northward-Type Connector
If you lot demand to run cablevision in excess of 150 feet, your installer may recommend either an LMR®600 or a "half inch" coaxial cable. These are extremely thick cables which are much more than industrial than whatsoever of the other varieties, and are expensive to boot. An installer will only recommend either of these in rare, specialized situations depending on individual need, but should they practice and then they will certainly have good cause. These are the best available cables to maintain a quality signal strength on the market.
The deviation between an LDF4 and an AI4 RPV-50 is the interior - the LDF4 has a foam covering, and the AI4 RPV-50 has zero. The difference in function, however, is minimal.

RG58 and RG174 Cables with SMA Connectors
RG58 and RG174 cables are used in vehicle boosters. The deviation between the two is the meliorate low-loss quality of the RG58 with cable length upwards to xx anxiety compared to the RG174'southward 6 feet. For large vehicles, such equally RVs or boats, the RG174 is preferred.
Both are fitted with SMA connectors. These are minor, copper connectors used in modems and the like. They are relatively inexpensive, which allow for the cable's cheaper cost.
The difference between the two is the better low-loss quality of the RG58 with cable length up to 20 ft compared to the RG174's max length of 6 ft.
Compatible with weBoost Drive 4G-M, weBoost Drive Sleek, and the weBoost Drive 4G-Southward.
Considerations Before You Purchase Cables

Earlier yous brand your coaxial cable buy, there are several things to consider. What device are yous using? A jail cell booster might crave a different cable than a satellite dish. Check the ohms, impedance and connections.
Next, calculate how far you need to go betwixt your devices or from the source of your power to the device. Refer to the section on cable length. Ordinarily, the shorter distance from your source to your device will produce a crisper signal.
Loss of signal is inevitable when traveling beyond any distance. A shorter cable will have less loss than a longer cable and a thicker cablevision will have less loss than a thinner cable, but they will all have some sort of loss. The loss that is acceptable volition depend on your devices and your application. To minimize the loss, the source and load impedances must be right. In order to calculate the amount of loss, use an online reckoner on the net, such as www.qsl.internet. Input your line type, line length, frequency, load SWR and power input. The matched loss, SWR loss, total loss and power out will be calculated. There are many calculators online and the formulas available to calculated manually.
We do non endorse this ane specifically. QSL Loss Estimator
Indicate Loss per x Feet
With increasing cable length more than point loss occurs. Betoken gain and loss is measured in decibels (dB). And decibels are measured exponentially. A loss of three dB means a weakened signal by 2x!

Per the chart, the Wilson400 (and the equally powerful RG11) has the best minimal loss and is almost twice as constructive compared to the RG6 for dwelling installations. The just cables mightier are the pricey LG600 and even pricier Half-Inch.
The RG174 should never be installed in any unit of measurement that needs more than than six feet of cable since it does a poor job of carrying signal at 10 anxiety.
Equally always, y'all can catechumen your cable installation with special cable connectors and adapters. However, to mix and match 50 ohm & 75-ohm cables and systems would lead to further signal loss, so it's best to stay consistent with the same type of relevant 50- or 75-ohm system and cables.
What is the deviation betwixt 50- and 75-ohm cables? This illustration might assist. Think of signal equally a drinkable and cables every bit straws. 75-ohm cables are your typical soda straws and l-ohm cables are those big gulp carnival straws.
Manufacturers of Coaxial Cable

Bolton Technical is a leading provider of coaxial cables, connectors and antennas used in high-stop electronics and equipment.

Wilson Amplifiers is the leading provider of cellular boosters. Cell phone boosters amplify 4G, LTE, and 3G for any telephone with any carrier for home, part, or vehicle.
We seriously detest dropped calls and poor coverage, so it'due south our goal in life to totally eliminate spotty betoken:
- Free consultation (ask u.s. anything) with our US-based customer back up (sales@wilsonamplifiers.com) or phone call us at ane-800-568-2723.
- Free aircraft.
- Better indicate or industry-leading 90 coin-back guaranteed. No questions asked.
- We want everyone to exist satisfied, then we provide lifetime technical back up and a 2-twelvemonth warranty for all products.
Ask united states annihilation and we'll be glad to aid.
LMR® is registered trademark of Times Microsystems.

THE WILSON AMPLIFIERS ADVANTAGE

FREE SHIPPING No Minumum Purchase

ninety-Mean solar day
Money Back Guarantee

LIFETIME
Technical Support
How To Repair A Cut Verizon Internet And Tv Wire Thst Was Buried,
Source: https://www.wilsonamplifiers.com/blog/understanding-coaxial-cables-the-complete-guide/
Posted by: vitalefords1948.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair A Cut Verizon Internet And Tv Wire Thst Was Buried"
Post a Comment